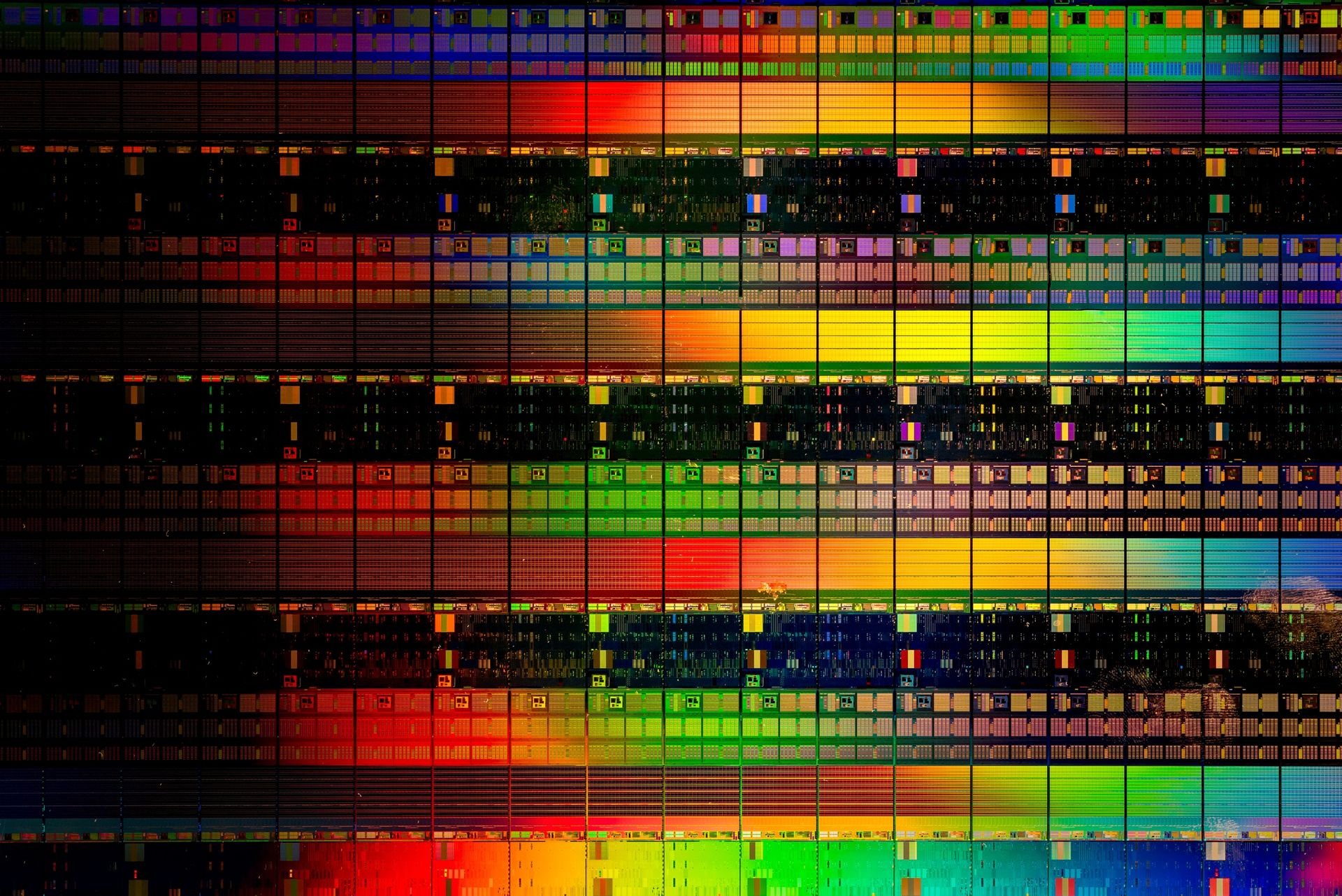
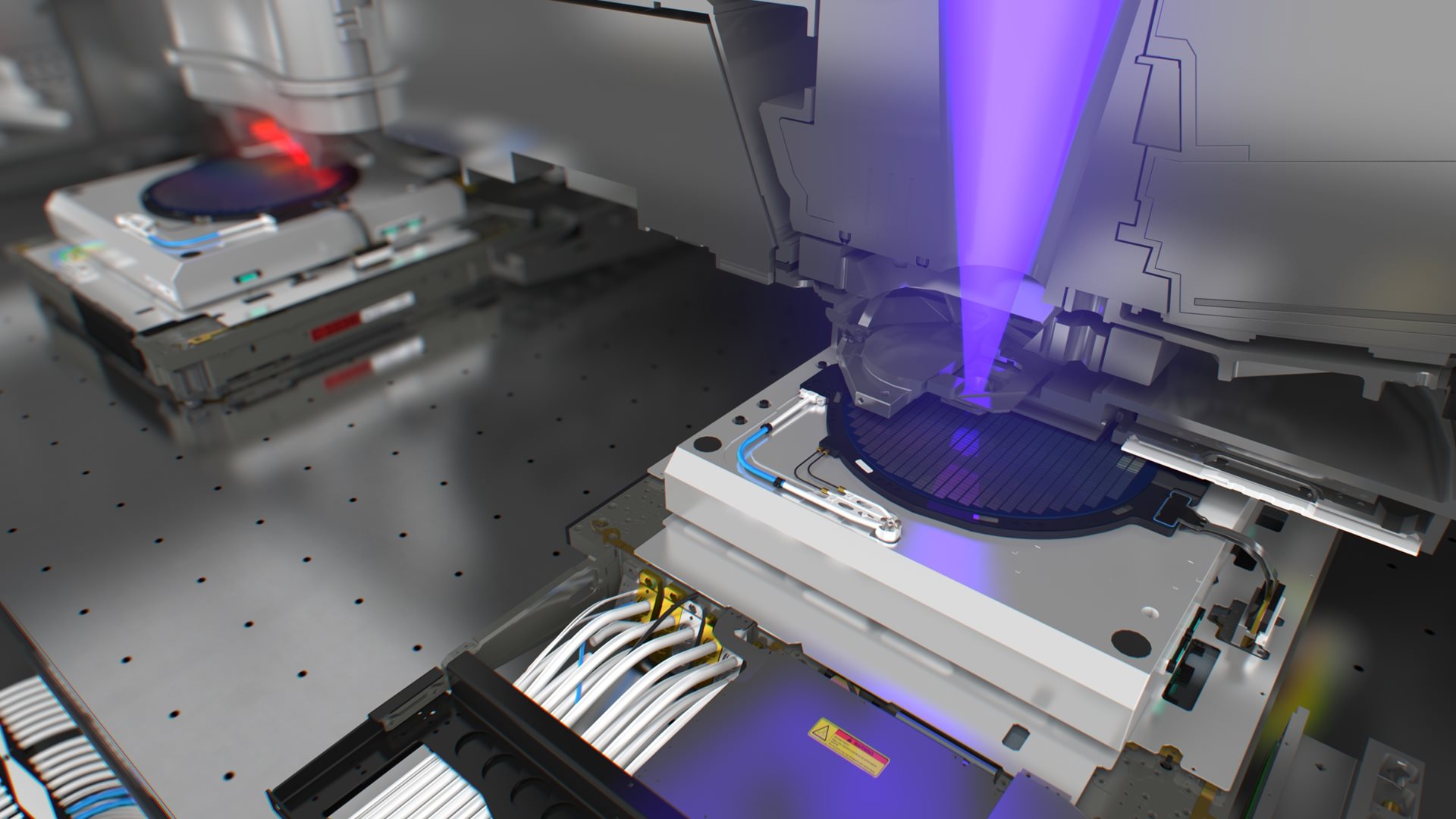
Microchips are made by building up layers of interconnected patterns on a silicon wafer.
The microchip manufacturing process involves hundreds of steps and can take up to four months from design to mass production. In the cleanrooms of the chipmakers’ fabs (fabrication facilities), air quality and temperature are kept tightly controlled as robots transport their precious wafers from machine to machine.
Tiny skyscrapers
Modern chips can have up to 100 layers, which all need to align on top of each other with nanometer precision (called 'overlay'). The size of the features printed on the chip varies depending on the layer, which means that different types of lithography systems are used for different layers. Our latest-generation EUV (extreme ultraviolet) machines are used for the most critical layers with the smallest features, and our DUV (deep ultraviolet) machines for the less critical layers with larger features.

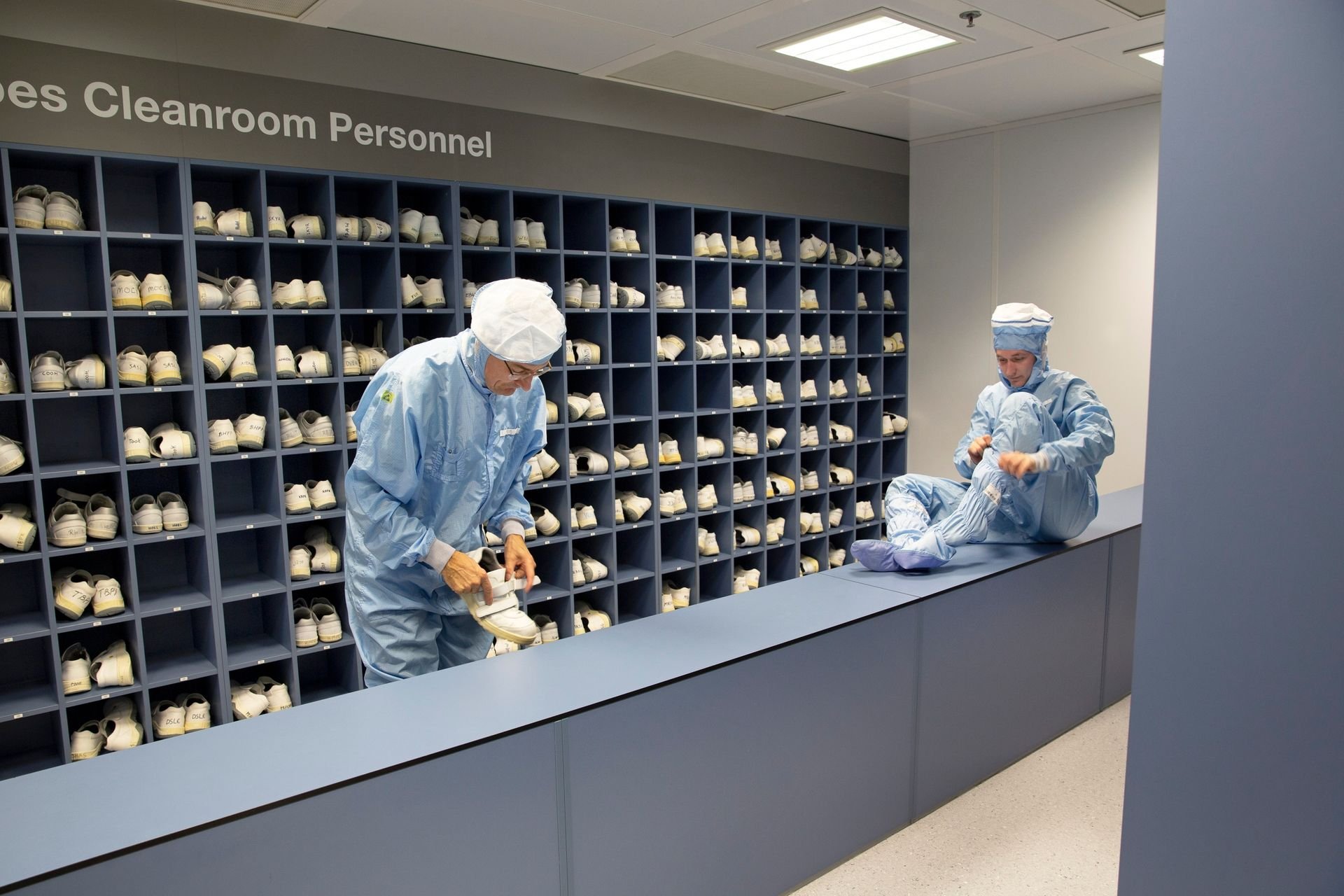
How clean is ‘clean’?
If even the smallest speck of dust or other foreign materials ends up on the wafer, it can ruin the microchip, so chipmakers are careful to keep their fabs clean. Just how clean? About 10,000 times cleaner than the outside air. Most chipmakers have ‘ISO class 1’ cleanrooms that are ‘zero dust’, meaning there are no more than 10 particles between 100 and 200 nm in size per cubic meter of air, and none larger than 200 nm. In comparison, a clean, modern hospital has about 10,000 dust particles per cubic meter.
The air inside a cleanroom is filtered and recirculated continuously, and employees wear special clothing (sometimes called ‘bunny suits’) to help keep the air particle free.
ASML machines are also made in cleanrooms inside our EUV and DUV factories in Veldhoven, the Netherlands.
Learn more about working in chipmaker fabs as a customer support engineer.

Types of chipmakers
Integrated device manufacturers (IDMs) such as Intel and Samsung both design and manufacture chips. Foundries, on the other hand, are companies that manufacture chips under contract for other companies. TSMC, GLOBALFOUNDRIES and UMC are examples of this type of chipmaker. A third type of chipmaker is the ‘fabless semiconductor company’ such as Qualcomm, Nvidia and AMD, who avoid the high costs of building and maintaining production facilities by focusing only on chip design. These companies might farm out their production to a foundry.
The crucial steps in semiconductor manufacturing
Now you understand the basics, it's time to take a deeper dive. Ready to learn about the six most crucial steps in making microchips?